What is portal
Portal is a web application that gathers information from various desperate sources to share the information among the users .
The portals has the following significant features
• collabaration
• security
• personalization
• customization
• search , etc
Site which are not portals are called vertical portal or Vortals
Windows share point services 3.0 is free licensing it has less feature compare to Moss 2007
Ghost able – stored in content database
Un ghost able – stored in hard disk
Web part
Web part is a custom control , created by a developer and deployed on to the share point site with the extension dwp or webpart(recommended) .
Web part zone
Web part zone is a logical area created by the designer on a web part page where the web part can be dropped.
Web part page
Page, which contain web parts.
There are two type of deployment
• stand alone Installation (Deployment ) – Everything is there in the same system .
• web form Installation ( Web garden) -
A Web garden is an application pool that is configured with more than one worker process. (Web gardens are to be distinguished from Web farms, which use multiple servers for a Web site.)
Hierarchy
Central administration
site administrator
Top-level sites
Top level site 1 - Top level site 2
Role
Administrator – can create sites, content, users, application, manage forms.
Designer – can create manage content and design of the website
Contributor – can only contribute to existing content .
Reader – no other permission except view.
Feature
Feature are new innovation in Moss 2007 these are plug gable component which actually modifies the structure, layout programming capability of share point site .
When you create a SharePoint site, it helps to understand where your site is in relation to the entire site hierarchy. The following three SharePoint concepts are important to know understand:
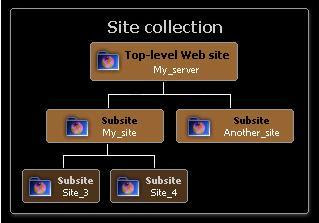
• Top-level Web site The default, top-level site provided by a Web server. To open the top-level Web site, you supply the URL of the server—for example, http://My_server — without specifying a page name or subsite. Administrators go to this site to change settings for the entire site collection.
• Subsite A complete Web site stored in a named subdirectory of the top-level Web site. Each subsite can have administration, authoring and browsing permissions that are independent from the top-level Web site and other subsites. A subsite can also have subsites of its own. Because every site below the top-level site is actually a subsite, each subsite is generally called simply a site. To open a subsite, you supply the URL of the server and any subsites—for example, http://My_server/My_site — without specifying a page name.
• Site collection A set of Web sites on a Web server, all of which have the same owner and share administration settings. Each site collection contains exactly one top-level Web site and can also contain one or more subsites. There can be multiple site collections on each Web server.
• SharePoint Online is the business collaboration platform for the Enterprise and the Web hosted by Microsoft. It provides the robust capabilities of Microsoft SharePoint Server as a cloud-based service that can help connect and empower people and reduce costs. By removing the operational burden that comes from managing the infrastructure associated with on-premises software your IT team can more rapidly respond to business needs and deliver sustainable competitive advantage for your organization.
• Application page: Allows the use of inline custom code. Application pages or "_layout" pages are stored on the SharePoint Web server and made available via a Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) virtual directory. Though application pages behave much like other ASPX pages and allow the use of inline custom code, they differ from content pages in that they cannot be used to host SharePoint features such as dynamic Web Parts and Web Part zones.
• Content type: A reusable collection of settings to apply to a certain category of content such as documents and folders. Content types are designed to help users organize their SharePoint content in a more meaningful way.
• Custom action: Represents a link, toolbar button, menu item, or any control that can be added to a toolbar or menu that appears in the UI. We define custom actions by using a custom action element within a feature definition file. We can bind custom actions to a list type, content type, file type, or programmatic identifier (ProgID).
• Event receiver: Evaluator of an event and definer of the behavior of an application. Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 allows us to define event handlers within libraries, lists, and sites. Event receivers can be defined by using a receiver element within a feature definition file.
• Feature: A package of Windows SharePoint Services elements that can be activated for a specific scope and that helps users accomplish a particular goal or task. Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 introduces this inherently portable and modular functionality, which simplifies modification of sites through site definitions.
• Master page: Pages that provide a consistent layout and appearance (look and feel) for SharePoint sites. They allow us to factor out layout, structure, and interface elements such as headers, footers, navigation bars, and content placeholders. Master pages in ASP.NET 2.0 and master pages in Windows SharePoint Services work in the same way.
• Module: A file or collection of file instances that define the location where the files are installed during site creation. Modules are frequently used to implement a Web Part Page in the site. We can define modules by using a module element within a feature definition file.
• SharePoint Web farm: A group of Office SharePoint 2007 servers that share the same configuration database. All site content and all configuration data is shared for all front-end Web servers in a server farm.
• Site definition: A set of files that includes a master XML configuration file that is stored on all front-end Web servers. A site definition provides the basic blueprint for how sites look, what lists they include, their default navigational structures, and so on.
• Site template: A package containing a set of differences and changes from a base site definition that is created through the UI or through implementation of the object model. The site template package is stored as a .cab-based file that can be downloaded or uploaded to site collections by users with the appropriate rights. Site templates offer a measure of portability to SharePoint applications.
• Solution: A file that is a bundling of all the components for extending Windows SharePoint Services in a particular way. A solution file has a .cab-based format with a .wsp extension. A solution is a deployable, reusable package that can contain a set of Features, site definitions, and assemblies that apply to sites, and that you can enable or disable individually. We can use the solution file to deploy the contents of a Web Part package, including assemblies, class resources, and other package components.
• Theme: A group of files (CSS, images) that allow you to define the appearance (look and feel) of Web pages. Themes in ASP.NET 2.0 and themes in SharePoint Products and Technologies work in the same way. Themes are used to help organizations to brand their portals and team sites. Office SharePoint Server 2007 includes a set of predefined themes. However, as a developer, we can create custom themes for our company.
No comments:
Post a Comment